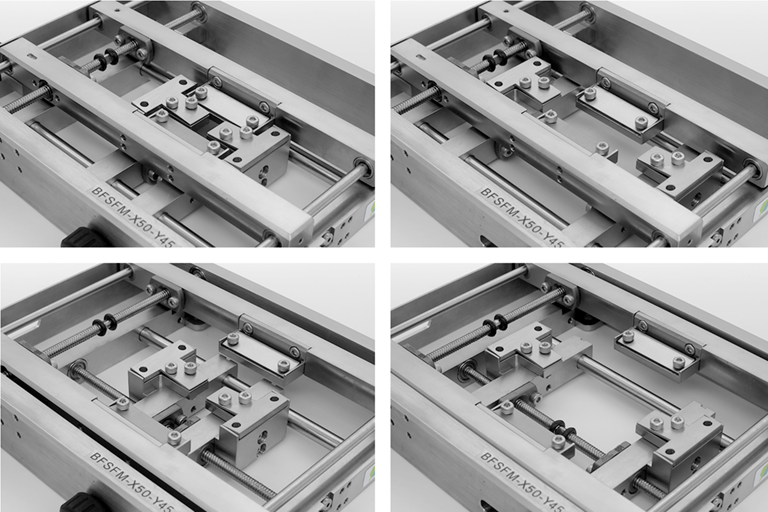
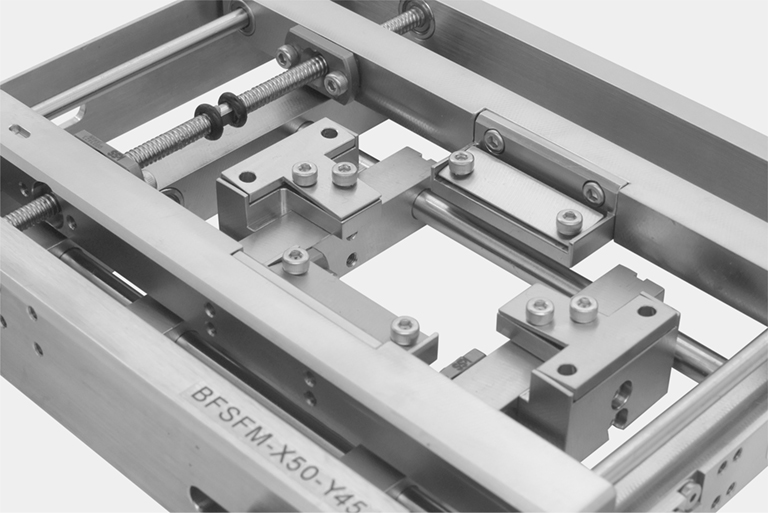
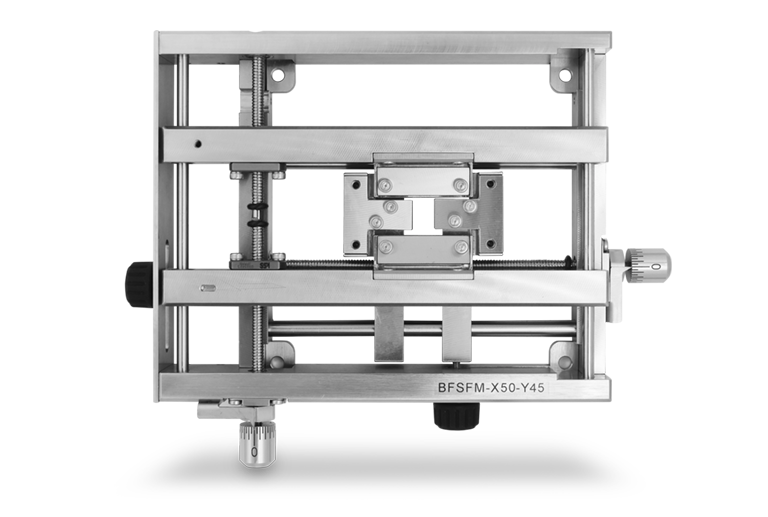
Lab tool
Biaxial Film Stretcher
for Microscopic Observation
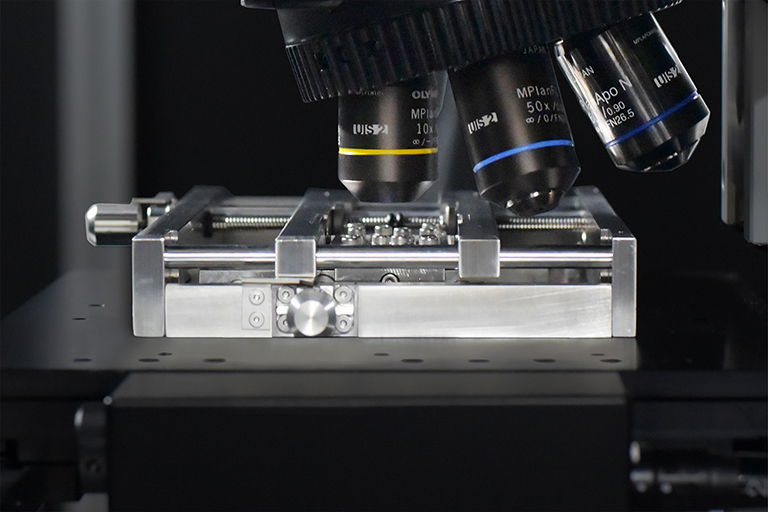
25 mm thickness fits on the microscope stage. A film can be stretched biaxially with its center fixed in a center of the field of view (FOV). Transmitted light can also be observed.
HIGHLIGHT
- Overview
- Specifications
- Other info
- User interviews
- Papers
Overview
This product stretches a polymer film biaxially offering users real-time microscope observation during the stretch. The frame of the stretcher is thin enough to be set between an objective lens and a sample stage of a microscope and, also enbales measurement of optical preperty of the film. Because the film is stretched from both ends, the observation area located at the center of both ends does not move with the stretch. The stretch can be controlled in x axis and y axis independently.

Generally, polymer films are molded by biaxial stretching to obtain optical properties such as transparency, mechanical strength properties against pulling and piercing, heat resistance and cold resistance. When evaluating the dynamics of structural changes in the biaxial stretching process of these polymer films, microscopic observation while stretching the sample and spectroscopic analysis such as polarized Raman spectroscopy and polarized infrared absorption spectroscopy are useful.
ScienceEdge's biaxial stretcher is designed with the optimum specifications for microscopic observation and various spectroscopic analyzes of such films.
Features
- Biaxial and independent stretch in x axis and y axis
- Thin structure (H=25mm) and settable on a microscope stage
- Structure enabling optical property measurement
- Stretch from both sides and fixed center
- High resolution of the stretch distance: ~ 0.05 mm
- Long stretch distance: > 45 mm
Applications
- Microscopic observation of film during stretch of polymer films
- Evaluation of polarization performance dependent on stretch of polymer films
- Evaluation of transmission spectrum dependent on stretch of polymer films
- Evaluation of Raman spectrum dependent on stretch of polymer films
Specifications
Configuration
- Biaxial Film Stretcher
- [Option] Motorization
Specifications
| Model | BFSFM-X50-Y45 |
|---|---|
| Film size | x ≧ 7 mm , y ≧ 12 mm |
| Stretch distance | x: 50 mm, y: 45 mm |
| Stretch resolution | 〜 0.05 mm (2.0 mm/1 rev.) |
| Power | Manual (Rotation knob) / [Option] Motorized |
| Rotation knob | Φ12 mm |
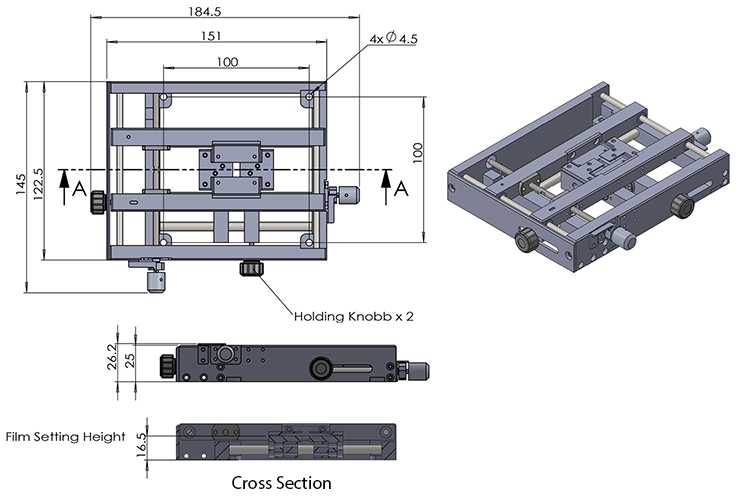
| Size (mm) | 151 x 122.5 x 25 (Frame), 184.5 x 145 x 26.2 (w/ knobs, needles) |
| Weight (kg) | 1.6 |
Vertical biaxial film stretcher (BFS-X20-Y20) is also available. See the image in the user interview page.
Drawing (mm)
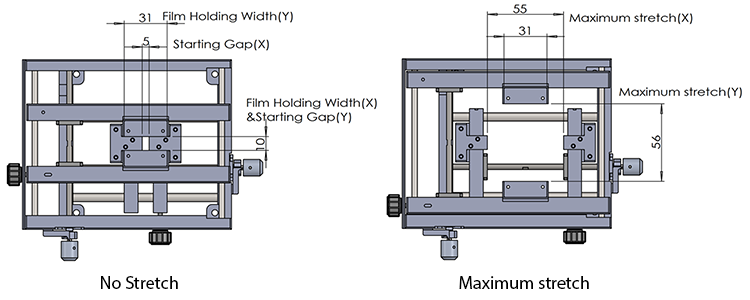
Others
Please ask your requests on the specifications such as the size, sample size, strech length, automation system and so on.
Other info
Scales for stretch distance
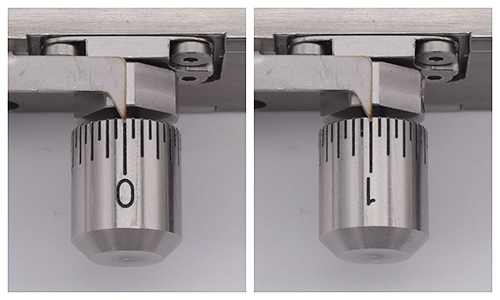
- Revolution scale(on the knob):0 ~ 2.0mm (1 rev.)/ 0.1 mm pitch/ The letters of 0 mm and 1 mm are printed at 0 ° and 180 °.
How to fix polymer film on the stage
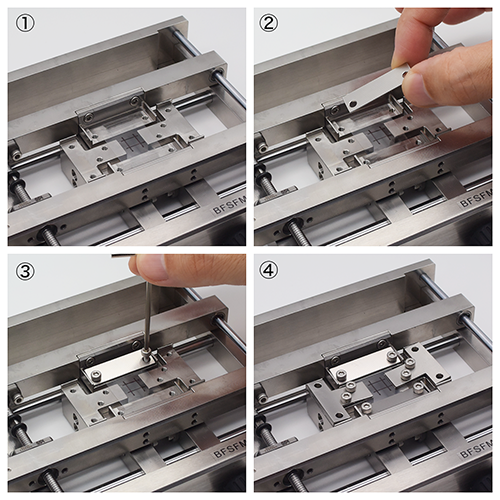
1. Set a film on the stage.
2. Put cover plates on the film.
3. Fix and press with screws.
Stetching films
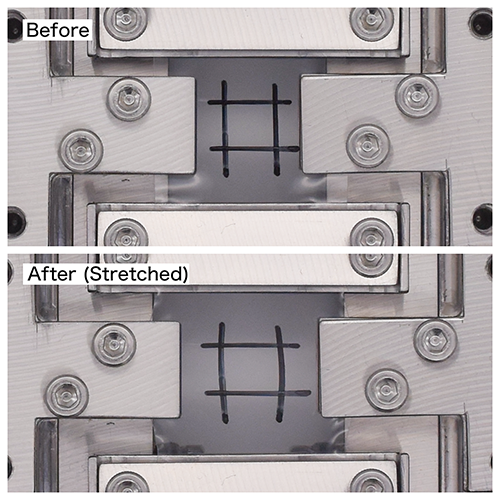
Picture of stretched polymer film in X axis and Y axis biaxially.
Fixing the stretched state of the film

If the film shrinks too much and you cannot maintain the stretched state when you take your hand off the knob, you can fix the stretched state by tightening the stopper tightly.
User interviews
Professor, Shizuoka University
"The resonance wavelength of surface plasmons depends on the structural period of the sample. Therefore, we thought that by stretching the sample and continuously changing its structural cycle, it would be possible to observe how the color of the light transmitted through the sample changes continuously.
ScienceEdge's Biaxial Film Stretcher was a device with the optimum specifications for the experimental system we were thinking of. Specifically, the sample can be widely stretched on two axes instead of one. Moreover, it is thin enough to be placed on a microscope stage for observation. There are very few biaxial stretchers on the market, and even if they are, they are very large devices, and they were not designed for observation with a microscope in the first place.
Also, what was good about actually using it is that both the X-axis and Y-axis are designed to stretch the sample in both directions at the same time. In other words, it is possible to stretch while keeping the observation site fixed in the center of the field of view of the microscope. Since ScienceEdge is a microscope professional, I felt that they had a good grasp of the functions and usability required for microscope observation." (Dec. 16th, 2021)
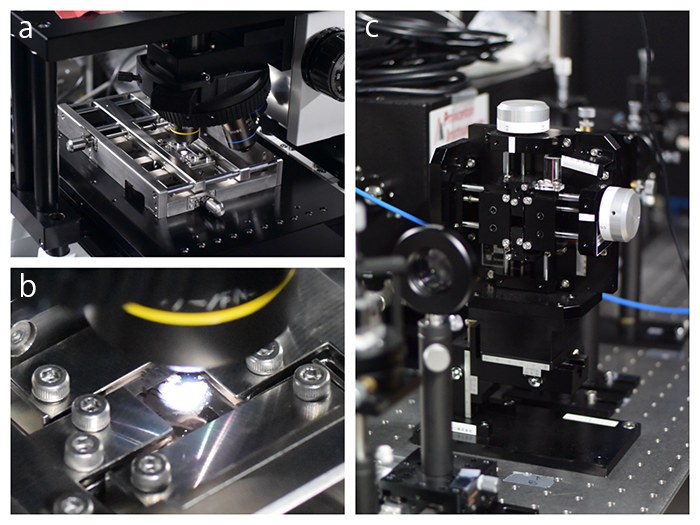
(a)(b)Biaxial Film Stretcher mounted on an actual experimental instrument. (c)Vertical Biaxial Film Stretcher that can be installed in the optical path (BFS-X20-Y20)
Papers
Ayana Mizuno and Atsushi Ono
“Dynamic Control of the Interparticle Distance in a Self-Assembled Ag Nanocube Monolayer for Plasmonic Color Modulation”
ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 4, 9, 9721–9728 (2021)
Ayana Mizuno and Atsushi Ono
“Static and dynamic tuning of surface plasmon resonance by controlling interparticle distance in arrays of Au nanoparticles”
Appl. Surf. Sci. 480, 846-850 (2019)